Dear All (and with thanks to Kevin Outterson for co-authoring this newsletter),
Post-newsletter addendum: A slide deck that summarizes the data from the paper is now available.
We talked in a 22 Mar 2021 newsletter about ensuring access to new antibiotics and you should take a moment to refresh your memory of its discussions of the report from CDDEP entitled “The State of the World’s Antibiotics in 2021”, the CARB-X Stewardship and Access Plan Development Guide, and ATM‘s release of its 2021 Access to Medicine Index.
Such discussions often include a tacit assumption that access is a problem limited to Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Well, this is simply not the case … in fact, ex-US access delays of several years (or more) are actually the norm around the world. To prove this point, a group of us have now published this paper (and discussion is available on YouTube):
- Outterson K, Orubu ESF, Rex J, Årdal C, Zaman MH. Patient access in fourteen high-income countries to new antibacterials approved by the FDA, EMA, PMDA, or Health Canada, 2010-2020. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2022 (doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab612). Yes, the actual published paper is dated 2022 (after this newsletter) as that’s when the paper came out in print. The new world of electronic publishing prior to in-print publishing can be confusing!
The paper analyzed the commercial availability in the G7 plus 7 high-income countries in Europe (CA, HR, DK, FR, DE, GR, IT, JP, NO, RO, ES, SE, UK, US) of the 18 antibacterial agents approved in the US, EU, Canada, or Japan during the decade of 1 January 2010 until 31 December 2019. The results are depressing:
- Most agents were accessible in only 3 countries (US, UK, SE), with the remaining 11 high-income countries having access to less than half of them.
- European marketing authorization did not lead to automatic European access, as 14 of the agents were approved by the European Medicines Agency but many fewer were commercially launched.
- Canada and Japan had the fewest commercial launches, just 2 and 5 of the 18, respectively.
- Shown visually, we have the display just below. The value in each cell is the number of days from approval in the US to commercial launch in that territory (except for lascufloxacin … see legend details):
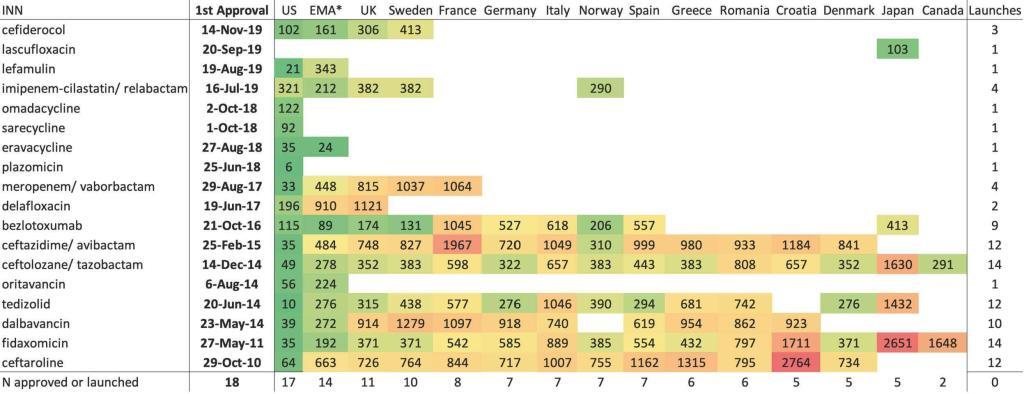
INN = international nonproprietary name; Empty cell = not commercially launched, except in the EMA column where empty cell = not approved by EMA; Number = lag from first approval to commercial launch, in days, except in the EMA column where number = lag from first approval to EMA approval, in days. The US was the country for all first approvals and first commercial launches, with the exception of lascufloxacin, approved and launched only in Japan. Color key: green = lowest lag in days; red = highest lag in days; yellow = 50th percentile lag in days.
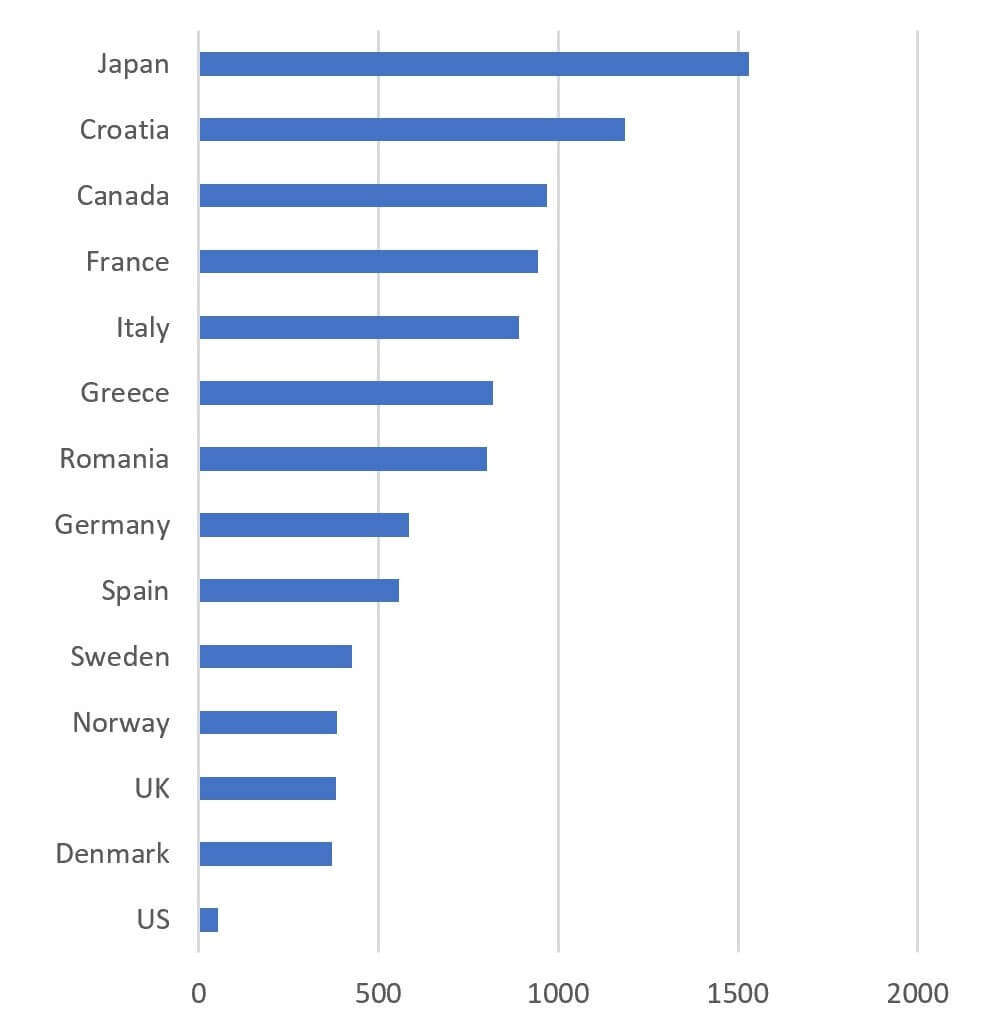
The data are even more disturbing when aggregated a bit … for the handful of drugs that are ultimately launched, the median lag to launch is in the range of several years (x-axis is median launch lag in days):
Of further interest, there was no significant difference in access between “innovative” and “noninnovative” agents (categorization used designations of “innovative” or “possibly innovative” by WHO or as “novel” by the Pew Charitable Trusts):
- “In total, four antibacterials were deemed “innovative” (lefamulin, meropenem/vaborbactam, ceftazidime/avibactam, and bezlotoxumab) and one “possibly innovative” (cefiderocol), but most of these five agents are not available in a majority of these countries.“
- Note that two of these five were selected by the UK Pilot and two were selected in the Swedish access program, but these markers of quality did not lead to commercial launch in a majority of the countries studied.
- “Comparing the four “innovative” and “possibly innovative” antibacterials with multiple launches (excepting lefamulin, launched only in the US) with the others, we found that there was no significant difference in median launch lags, p=0.465, among all eleven antibacterials with launches in more than one country.”
- Net, antibacterials considered more innovative were not commercial launched more quickly.
- Satisfying important clinical needs is also a goal of antibacterial developers, and one potential proxy for that is placement on the WHO Essential Medicines List, but placement on the EML actually was correlated with a slower commercial launch, p=0.043.
- WHO has also categorized antibacterials as Access, Watch, or Reserve (AWaRe). Of the antibacterials on the AWaRe list, all but one are in Reserve. It is hard to make money if the drug is held in reserve, unless revenues are delinked from volume.
FInally (and no surprise), median annual sales in the first launched market (generally the United States) for these 18 antibiotics were low, $16.2M. The entire class of antibacterials — 18 in total — had combined annual sales in their largest market (generally the US) totaling just $714M. The fruit of a decade of work, the fulfillment of the IDSA “10 x ’20” target, was given a valuation by the market less than a single new oncology drug.
—
This is clearly unacceptable and requires several parts of the ecosystem to collaborate in applying the fix.
- First, antibacterial R&D is hard work and we need to encourage talented people to enter this area: FDA’s analysis of 40 years of antibacterial R&D (Dheman et al.) shows falling success rates and rising R&D timelines. Push funding such as CARB-X, Novo REPAIR Impact Fund, and the AMR Action Fund are (hopefully) attracting talent but this alone is not enough.
- As was demonstrated when Cipla walked away from EMA approval of plazomicin due to financial infeasability of the work requested by EMA, the innovator company can only carry a portion of the burden: post-approval costs are $300-400m over the first 10 years to simply maintain the product in your pharmacy — without income, there can be no product.
- At a regulatory level, the current system of country-by-country approvals decisions is both costly and slow. The EMA’s centralized process points the way to multi-country approvals; further such consortia are possible as shown by the recently created Australia-Canada-Singapore-Switzerland-United Kingdom (Access) Consortium.
- Approval does not, however, equal access … there is also reimbursement as a final step. The tool needed here is the creation at the political level by the G7 and G20 economies of substantial pull incentives such as the UK (NHS England) subscription pilot and the PASTEUR Act in the US.
—
Can all of this happen? Well, momentum does seem to building:
- The UK pilot appears to be solidly underway.
- It’s a work in progress, but we are hearing encouraging things about the political process for PASTEUR in the US.
- There are clear signs (24 June 2021 newsletter) that the EU is getting going on the pull incentives for antimicrobials proposed in its ambitious Pharmaceutical Strategy.
- India’s publication of a Priority Pathogen List suggests that they are getting into the game.
- The AMR Action Fund makes it clear that the next 5-10 years are pivotal:
- “Putting the necessary policy reforms in place will take time”
- ” The AMR Action Fund will bridge innovative candidates in the pipeline through the most challenging later stages of drug development, ultimately providing governments time to make the necessary policy reforms to enable a sustainable antibiotic pipeline.”
Please keep doing your bit in your corner of the ecosystem! With fingers crossed for steady progress and all best wishes, John and Kevin
John H. Rex, MD | Chief Medical Officer, F2G Ltd. | Operating Partner, Advent Life Sciences. Follow me on Twitter: @JohnRex_NewAbx. See past newsletters and subscribe for the future: https://amr.solutions/blog/. All opinions are my own.
Kevin Outterson, JD, Professor of Law, Boston University & Executive Director, CARB-X (these views are personal and do not necessarily reflect the views of CARB-X or any of its funders) @koutterson
Current funding opportunities (most current list is here):
- CARB-X recently announced that their existing resources will be reserved to fund their existing portfolio (more than 80 total awards, and counting, as they include contracting from prior rounds). New rounds from CARB-X will occur only after new funding is obtained in 2021.
- It’s not a funder, but AiCuris’ AiCubator offers incubator support to very early stage projects. Read more about it here.
- The Global AMR R&D Hub’s dynamic dashboard (link) summarizes the global clinical development pipeline, incentives for AMR R&D, and investors/investments in AMR R&D.
- In addition to the lists provided by the Global AMR R&D Hub, you might also be interested in my most current lists of R&D incentives (link) and priority pathogens (link).
Upcoming meetings of interest to the AMR community (most current list is here):
- 24-26 Aug 2021 (virtual, EU-centered timings): The 5th edition of the annual AMR conference sponsored by the BEAM Alliance, CARB-X, the Novo REPAIR Impact Fund, the IMI Accelerator, and the European Biotechnology Network. The in-person version of this meeting is consistently excellent; the video-based version will have to do for 2021. Go here for details.
- 30 Aug – 1 Sep 2021 (virtual, East Coast US timings): FDA (CBER)-NIAID-sponsored workshop entitled “Science and Regulation of Bacteriophage Therapy.” Go here for details and to register.
- 1-2 Sep 2021 (virtual, 10a-3p EST on both days): FDA -sponsored workshop entitled “Advancing the Development of Pediatric Therapeutics (ADEPT 7) Complex Innovative Trial Design.”
- In brief, “The Complex Innovative Trial Design Pilot Meeting Program (CID Program) facilitates and advances the use of complex and innovative trial designs that have the potential to optimize drug development in small populations.
- “Innovations that have been proposed include Bayesian and other methods of utilizing external historical information from previous pediatric trials or other populations (such as adults), adaptive designs, bridging biomarkers, etc.”
- “The workshop will specifically focus on two topics of interest: bridging biomarkers in pediatric extrapolation and Bayesian techniques in pediatric studies. In addition, the workshop will allow for an open dialogue around the use of these approaches among regulators, industry, academia, and patient organizations.”
- Looks fascinating. Go here for the detailed Federal Register notice and here to register.
- 30 Sep 2021 (virtual, 9a-noon EST, 2-5p BST): Featuring Dame Sally Davies and Marc Mendelson, this is a Vivli-sponsored workshop entitled “A Foundation Briefing on Industry AMR Surveillance: Data for Action” that will discuss Vivli’s new surveillance sharing platform. Go here to register.
- [NEW] 8 Oct 2021 (Boston, in person, 9a-6.30p, COVID vaccination required): 8th annual BAARN (Boston Area Antimicrobial Research Network) meeting. Go here for details; registration link is pending.
- 8-11 Oct 2021 (Aberdeen, Scotland): 10th Trends in Medical Mycology. Go here for details.
- 11-15 Oct 2021 (physical, somewhere in the UK): UK-focused Innovation Mission sponsored by Innovate UK in collaboration with AMR Insights and Oxford innovation. This free event seeks to connect AMR-focused start-ups, SMEs and Multinationals, Academia, Research Institutes, Regional Development Companies and other interested stakeholders in the UK, Europe and other parts of the world. Go here for more details.
- 16-24 Oct 2021 (Annecy, France): Interdisciplinary Course on Antibiotics and Resistance (ICARe). This is a soup-to-nuts residential course on antibiotics, antibiotic resistance, and antibiotic R&D. The course is very intense, very detailed, and gets rave reviews. Registration is here and is limited to 40 students. Bonus feature: For obvious reasons, the course didn’t happen in 2020! But as a celebration of the course’s 5th year, a webinar version was held on 29 Oct 2020: go here to stream it.
- 5-8 Nov 2021 (Albuquerque, New Mexico): Biannual meeting of the MSGERC (Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium). Save-the-date announcement is here, details to follow.
- 6-11 Mar 2022 (Il Ciocco, Tuscany): Gordon Research Conference entitled “New Antibacterial Discovery and Development”. Go here for details, go here for the linked 5-6 Mar Gordon Research Seminar that precedes it.
- 9-13 May 2022 (Athens and online): 40th Annual Meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, Go here for details.
- 20-24 Sep 2022 (New Delhi): 21st Congress of the International Society for Human and Animal Mycology (ISHAM). Go here for details.
- 25-28 Oct 2022 (Stellenbosch, South Africa): The University of Cape Town’s H3D Research Centre will celebrate its 10th anniversary with a symposium covering the Centre’s research on Malaria, TB, Neglected Tropical Diseases, and AMR. Go here to register.